Jesse, at Le Cafe, reports on the bubble made in China. (If you missed my interview with Jesse, it’s posted here and here, my space on Seeking Alpha.) – Ilene
Of Bubbles and Busts: Which Way for China?
Courtesy of Jesse’s Café Américain
"Mischief springs from the power which the monied interest derives from a paper currency which they are able to control, and from the multitude of corporations with exclusive privileges…which are employed for their benefit." Andrew Jackson
While the crowd has been chortling over the anticipated decline and fall of the American Empire, they may also be overlooking the dangerously unstable bubble in China, and the implications for that phenomenon when the global economy shifts again.
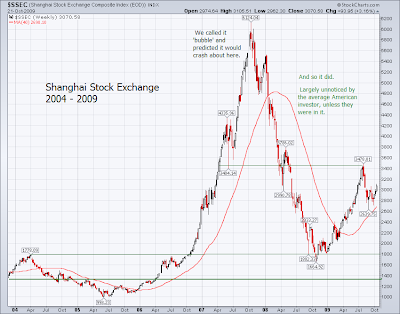 There has been little doubt in our minds for a long time that China was in an impressive growth cycle that was fueled by overly cheap money and a spectacular equity bubble. This is why we posted that documentary about the Crash of 1929 yesterday, in commemoration of the 80th anniversary of Black Thursday. The collapse of bubbles will not be in the US alone, and the description and atmosphere as described in that film sounds much more like China today than it does the US.
There has been little doubt in our minds for a long time that China was in an impressive growth cycle that was fueled by overly cheap money and a spectacular equity bubble. This is why we posted that documentary about the Crash of 1929 yesterday, in commemoration of the 80th anniversary of Black Thursday. The collapse of bubbles will not be in the US alone, and the description and atmosphere as described in that film sounds much more like China today than it does the US.
The reasoning behind this is fairly straightforward.
It may be hard to remember from the current lofty heights of the ‘China miracle’ but their economy was a train wreck in the latter part of the 20th century. Prior to 1980 the state owned People’s Bank controlled all the financial resources of the command driven economy. The government created State Chartered Banks (SCB’s) in the 1980’s, but their business activities were still driven by state policy initiatives, and they quickly became burdened by bad debts. A speculative push and some tax breaks for foreign direct investment helped to further distort the economy, which led to a severe domestic slump, with banks burdened by Non-Performing Loans. But it was still a centralized economic regime, with a reminder served by the brutal suppression of the student demonstrations in Tiananmen Square in 1989.
In 1994 China tried to cure the serious problems in their domestic economy by devaluing the yuan from 5 to 8.3 to the US dollar in order to facilitate an export driven recovery. That is a 40% devaluation! All your costs were just marked down 40% relative to the competition.
China was able to make key investments in the 1996 Democratic party campaign, and Bill Clinton championed China’s favored nation status in 1998, smoothing the way for China’s admission into the World Trade Organization in 2000, while still maintaining a deeply devalued currency that was ‘pegged’ to the US dollar. As a general note, a country does not engage in unrestricted trade with another country that maintains a currency peg after a devaluation, unless there is some significant ulterior motive. The rational economic response is to first maintain trade tariffs to control the flow of goods and the de facto subsidies and barriers imposed by an artificially manipulated currency. Whenever anyone says that a currency that is ‘pegged’ and subject to tight exchange controls is not manipulated, except in highly unusual circumstances such as a gold standard, the people in the room just should laugh them on their way out the door.
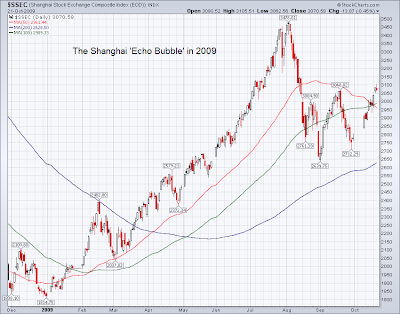 Pegging the yuan to the dollar helped to encourage foreign direct investment, and helped to stabilize the artificially low prices that US importers could achieve, most notably the Arkansas based WalMart.
Pegging the yuan to the dollar helped to encourage foreign direct investment, and helped to stabilize the artificially low prices that US importers could achieve, most notably the Arkansas based WalMart.
Those are the roots of the China bubble: cheap money. It used to be said that the Japan Miracle was a result of their real estate price explosion, the ‘monetization of the land.’ This is a bit of an oversimplification since it was a bubble fueled by government industrial policy known as mercantilism. But using this analogy, China was monetizing the cheap labor of its people, as a means to provide cheap goods to the West, and allow business to erode the wage gains which labor had achieved through the worker’s union movements of 1930 to 1970. And if one looks at the progress of the US median wage from 1980 to 2009, it worked. The US middle class is flat on its back.
All that history aside, what is going to happen now with China? It was important to take some time to establish the roots of its current bubble, because people have become wide-eyed and accepting of the miracle. Yes, cheap labor helps, but there are plenty of countries around the world that have cheap labor. It tends to get less cheap when the country develops, and when the domestic economy and education and infrastructure improves, while the government can continue to provide subsidies via tax breaks and cheap currency and subsidized debt from banks that are still controlled by the State.
The trade surpluses that have created China’s enormous two trillion dollar reserves are a direct result and indicator of the China bubble formulated by Western banks and a domestic government made increasingly nervous by popular unrest due to their economic blundering. Those surpluses in turn have fueled a monumental asset bubble in China that they must handle with care.
The China miracle is a new paradigm in the same way that the tech bubble introduced a new era of permanent prosperity in the US in 2000, and trading margin created a vibrant US economy in 1929. There are many true believers in this miracle, most notably Jimmy Rogers, but that does not mean it is not simply what it is: a bubble created by monetary and policy manipulation.
China is faced with a period of transition. It must move from a export economy to a more balanced domestic consumption economy. This will raise living standards and education levels, and disposable incomes of its people. If a ruling party is an oligarchy, whatever political label one wishes to attach to it, then they are often jealous and insecure of their power base, and anxious about losing control.
If there is a continuing collapse in trade, and the world economy, the theory of decoupling promoted by analysts like Peter Schiff appears to be exceptionally unlikely, unless China can make the transition to either a regional predatory power or more domestically self sufficient.
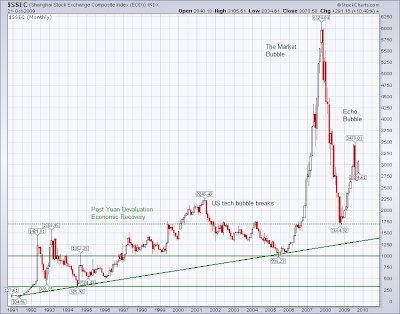 China can do this, but it is quite important to remember that they do not have market capitalism at their backs and a history of well regulated banks and markets to help them allocate their new found riches in productive, non-corrupt ways. The China miracle is highly dependent on Western multinationals.
China can do this, but it is quite important to remember that they do not have market capitalism at their backs and a history of well regulated banks and markets to help them allocate their new found riches in productive, non-corrupt ways. The China miracle is highly dependent on Western multinationals.
In some dimensions, China is more like the US in 1929 than the US itself resembles that paradigm today. This would imply that China is more likely to experience the kind of devastating crash and long economic Depression if world trade collapses. As you may recall, the US was a heavy net exporter and an economic miracle itself in the 1920s having largely escaped the economic devastation of the first World War.
Perhaps this is a long way of saying that the outcome for China is hardly pre-determined, but it is not nearly so rosy as the believers in the miracle might think. They will have a choice, but that choice is going to lead them to a crossroads quickly, between becoming a free nation with a burgeoning middle class that is increasingly free to make its own choices, or a military dictatorship that seeks to establish client states to provide raw materials and receive its manufactured goods in return.
We should expect the ‘One World Government’ crowd to make another play when things get particularly bad. Never waste a crisis. The oligarchies do not particularly care whether your flag is red, yellow, or red, white and blue, as long as they are in control. Early on Bill Gates went to China, and upon his return said, "This is my idea of capitalism." The China Bubble and the Convergence of Oligarchies
So, in summary, there is a great deal of facade around the China miracle that is of recent and somewhat more shaky construction than most people realize. The Chinese economy is still highly artificial and centrally controlled, with enormous rot underneath that shiny facade in the form of bad debts, malinvestment and over capacity in some areas with insufficient development in others.
China will continue on, as well as the US. The question is really about how and what they will become, and what investment opportunities and perils they represent to the individual. Will the yuan appreciate if the economy collapses into a nasty deflation, as the deflationary theorists think happens when a currency credit bubble breaks? Oh, if only life were that simple and linear. The strength of a currency can fluctuate short term in response to temporary contractions and squeezes, as the US dollar had done in reaction to the eurodollar short squeeze caused by the collapse of dollar securitized debt assets and some remarkably bad risk management practices by the large European banks.
At the end of the day, a currency is going to be supported by the underlying value of what it represents, because unless it is specie, that is all it represents. And in many ways this is one of the most quiet, almost hidden reasons for the rush to commodities and the bull market in gold. Investors around the world are running from bubbles and monetary manipulation, and seeking safer harbors in those things that have undeniable value and usefulness, or have stood the test of time as nations and currencies have risen and fallen.
Empires may dwindle, but bubbles collapse, and sometimes spectacularly.



