One would not know it from looking at the S&P which just hit a 2023 high, but there is a bit of a bankruptcy crisis sweeping the US where companies are filing for bankruptcy at the fastest pace in 13 years, in a clear sign of a tightening credit squeeze as interest rates rise and financial markets have locked out all but the strongest borrowers.
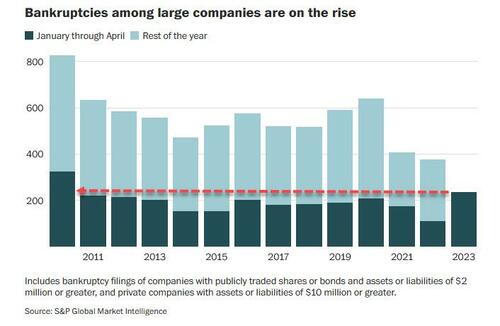
The increase is most visible among large companies, where there were 236 bankruptcy filings in the first four months of this year, more than double 2022 levels, and the fastest YTD pace since 2010 according to S&P Global Market Intelligence.
Several large recognizable companies with hundreds or thousands of workers have filed for bankruptcy protection in recent weeks, including Bed Bath & Beyond and Vice Media, although their financial troubles predated the recent economic turmoil.
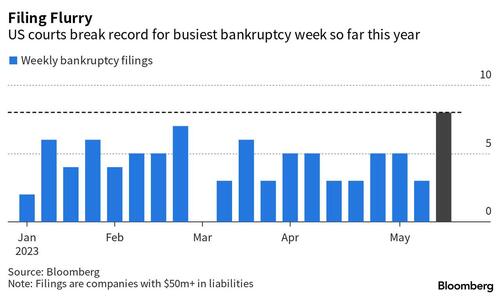
The bankruptcies did not slow down in May, when just the past week saw eight companies with more than $500 million in liabilities file for Chapter 11 bankruptcy, including five in a single 24-hour stretch last week, making this the busiest week for chapter 11 filings so far this year. In 2022 the monthly average was just over three filings.
Last week’s eight large filings, those with at least $50 million of liabilities, included those of now defunct woke “media empire” Vice Media, Envision Healthcare and Monitronics International. Prior to last week, the busiest seven-day stretch this year belonged to a week in late February that saw firms including Covid-19 testmaker Lucira Health, generic drugmaker Akorn and former SPAC Starry Group kick off insolvency proceedings
In total, twenty-seven large debtors have filed for bankruptcy so far in 2023 compared to 40 for all of 2022, according to figures compiled by bankruptcydata.com.
Among all types of companies, large and small, the increase in bankruptcies is somewhat more muted, with filings remaining below pre-pandemic levels and historic norms, according to Mark Zandi, chief economist at Moody’s Analytics. However filings, especially among large, unprofitable companies, are ramping at a frenzied pace as interest rates rise, pandemic-era government support dries up and sales growth slows amid a cooling economy.
There were about 16,200 bankruptcy filings among all types of companies in U.S. District Courts in the first quarter — up from 12,200 a year earlier, but still well below the 21,000-or-more-a-quarter in the pre-pandemic period, data from Moody’s Analytics shows. Even those pre-pandemic numbers were relatively low in historic terms, in part because low interest rates made it easy for companies to borrow.
Now, S&P Global forecasts that the 12-month trailing default rate for speculative-grade securities will jump from the current 2.5% to 4.5% by early 2024.
“The era of low interest rates and pandemic-related government support programs helped keep companies afloat that may have otherwise had few other options,” S&P analysts said of their large-company data. “Now that interest rates are back to pre-Great Recession levels and pandemic support programs are largely over, we’re seeing a fresh uptick in a possible sign that companies are running out of time.”
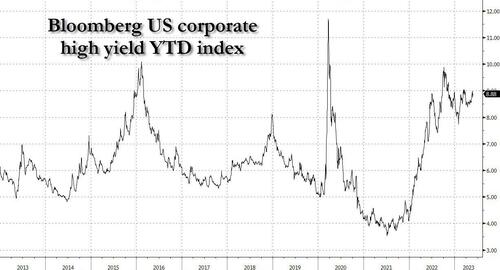
Yields on junk bonds have more than doubled from less than 4% in mid-2021, as measured by the Bloomberg US High Yield Index. The Fed has warned that lenders could further contract the supply of credit to businesses after recent turmoil in the banking sector.
“Our general view is that we are going to see an increase in ‘hard restructurings’, driven by the combination of higher debt levels from the borrowing binge of Covid and rising interest rates. The triggers will be running out money and inability to refinance maturing debt,” said Bill Derrough, an investment banker at Moelis who advises clients across distressed situations. “Some companies have used every trick in the book and now have run out of tricks.”
Companies that sell nonessential consumer items have been harder hit than other sectors as Americans curb their spending amid high inflation, S&P said. Plant-Based Pizza Boston, catalogue retailer AmeriMark Interactive and the Party City retail chain are among the recent casualties.
Last month, the dress retailer David’s Bridal filed for bankruptcy for the second time in 5 years, and said it was seeking a buyer, days after informing state labor departments that it planned to lay off more than 9,000 employees nationwide. The 70-year-old company said its business was weighed down by “the post-covid environment and uncertain economic conditions.”
Perhaps the most notable recent bankruptcy was that of long-struggling Bed Bath & Beyond, which filed for bankruptcy in late April, got a boost from the wave of consumer spending during the pandemic — when Americans spent more time at home. But when the economic climate shifted and stubbornly high inflation reduced discretionary purchases, the retailer’s fortunes tumbled.
Recent filings make clear how some large, indebted companies were clobbered by the end of easy money. A Vice Media bankruptcy filing last week disclosed that the company had been cash flow negative for several years, forcing it to borrow heavily to fund operations. As interest rates rose, it became costlier for Vice to refinance those loans. For a delightful read on the collapse of the faux-woke media empire, which at one point was valued by idiots at almost $6 billion, read the following FT report.
Turmoil in the banking business in March also contributed to a small rise in bankruptcy filings in that sector this year, S&P said. The most notable filing was SVB Financial Group, the parent company of Silicon Valley Bank, which collapsed after a run on the bank’s deposits.