Antarctic heat, wild Australian winter: what’s happening to the weather and what it means for the rest of the year
Australia’s south and east have seen freezing temperatures and wild weather this winter. At the same time, the continent as a whole – and the globe – have continued to warm.
What’s going on? As ever, it’s hard to pinpoint a single cause for weather events. But a key player is likely an event unfolding high above Antarctica, which itself may have been triggered by a heatwave at surface level on the frozen continent.
Here’s what’s happening – and what it might mean for the rest of this year’s weather.
When the stratosphere heats up
Out story begins in the cold air over Antarctica. July temperatures in the stratosphere, the layer of air stretching between altitudes of around 10 and 50 kilometres, are typically around –80°C.
The winds are also very strong, averaging about 300 kilometres per hour in winter. These cold, fast winds loop around above the pole in what is called the stratospheric polar vortex.
Occasionally, persistent high air pressure in the lower atmosphere can influence large-scale waves that extend around the globe and up into the stratosphere. There they cause the strong winds to slow down, and the air high above the pole to become much warmer than normal.
In extreme situations the stratospheric winds can completely break down, in what is called a “sudden stratospheric warming” event. These events occur every few years in the northern hemisphere, but only one has ever been observed in the south, in 2002 (though another almost happened in 2019).
Pushing polar weather our way
Once the polar vortex is disturbed, it can in turn influence the weather at the surface by steering weather systems from the Southern Ocean towards the Equator. However, this is a slow process.
The impact at the surface may not be felt until a few weeks or even months after the initial weakening of the stratospheric polar vortex. Once it begins, the stratospheric influence can prevail for more weeks or months, and helps meteorologists make long-range weather forecasts.
In climate science terms, the weak stratospheric winds put an atmospheric system called the Southern Annular Mode into a negative phase. The main effect of this on surface weather is to bring westerly winds further north.
In winter, this means polar air outbreaks can reach places like Sydney more easily. As a result, we see more rain over much of southern Australia, and snowfall in alpine regions. In spring and summer it means westerly winds blow over the continent before reaching the east coast, bringing warm and dry air to southeastern Australia.
The exact impact of a weaker polar vortex depends on how much and for how long the weather systems are being pushed further northward. It will also depend on other weather influencers such as El Niño and the Indian Ocean Dipole.
This winter’s weirdness
Unpicking exactly why any weather event occurs is tricky at the moment, because global weather has been absolutely crazy over the past 12 months or so. Global temperatures are much higher than usual, which is making unusual weather very common.
But there are indications that the stratosphere is having some influence on our weather this winter.
The stratospheric polar vortex started to warm in mid-July, and is about 20°C warmer than the long-term average. At the time of writing, the winds slowed down to about 230 kilometres per hour, 70 kilometres per hour slower than average.
These numbers mean that, technically, the event does not qualify as a sudden stratospheric warming. However, further warming may still occur.
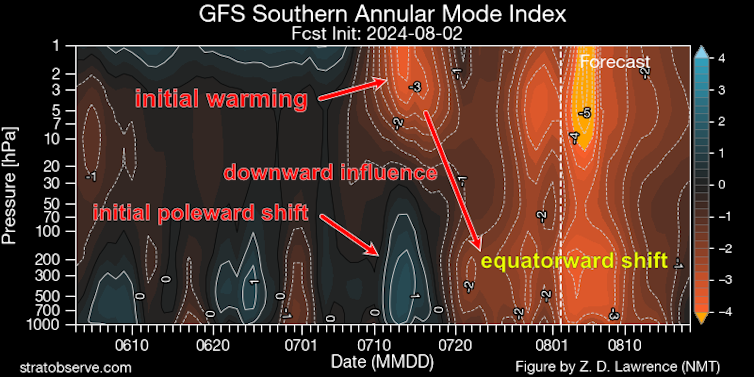
If we look at how southern hemisphere winds have evolved in the past few weeks, we see a pattern which looks like what we would expect from a sudden stratospheric warming.
First, we see warming in the stratosphere which is at first accompanied by a poleward shift of weather systems.
The stratosphere’s influence then propagates downward and seems to induce many weeks of weather systems shifted towards the equator.
This coincides with the period of cold and rainy weather along Australia’s east coast in late July and the beginning of August. Forecasts suggest the Southern Annular Mode will be a long way from normal conditions in the first half of August – four standard deviations below average, which is extremely rare.
A surface disturbance
The main reason for the polar vortex to slow down is disturbances from the surface. Weather over the Amundsen Sea near Antarctica in the South Pacific is an important source of these disturbances.
This year, we have seen disturbances of this sort. There have been near-record surface temperatures around Antarctica.
These disturbances may be due to the globally high ocean temperatures, or even lingering effects of the eruption of the Hunga Tonga volcano in 2022. But more research will be required to confirm the causes.
What should we expect for the rest of the year?
There are two pathways until the end of the year. One is that the stratospheric winds and temperatures recover to their usual values and no longer influence surface weather. This is what the forecasts from Ozone Watch seem to suggest.
Another is that the stratosphere keeps warming and the winds keep being slower all the way into summer. In this scenario, we would expect a persistent negative Southern Annular Mode, which would mean a spring and potentially even summer with warmer and drier than usual weather over southeastern Australia, and a small ozone hole.
The seasonal forecasting models from the European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts seem to favour this second scenario.
![]()
Martin Jucker, Senior Lecturer in Atmospheric Science, UNSW Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.




